- The Indian Rupee weakens to near an all-time low in Tuesday’s Asian session.
- Rising US bond yields and a weaker Chinese Yuan could undermine the INR, but the RBI’s intervention might help limit its losses.
- Traders brace for the US November Retail Sales on Tuesday ahead of the Fed rate decision.
The Indian Rupee (INR) edges lower to near a fresh record low on Tuesday. A rise in US Treasury bond yields and weakness in the Chinese Yuan exert some selling pressure on the local currency. Furthermore, the widening of India’s merchandise trade deficit in November further weighs on the INR.
Any significant depreciation of the Indian Rupee might be limited as the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) will likely sell the USD via state-owned banks to avoid excess volatility. The US November Retail Sales is due later on Tuesday. All eyes will be on the US Federal Reserve (Fed) interest rate decision on Wednesday for fresh catalysts. Also, the Fed Chair Jerome Powell’s press conference and the updated economic projections will be closely monitored.
Indian Rupee remains weak on the back of global cues
- The Indian WPI inflation eased to a three-month low of 1.89% in November from 2.36% in October, the Ministry of Commerce and Industry showed on Monday. This figure came in softer than the expectation of 2.2%.
- The preliminary estimate released by HSBC showed on Monday that the India Manufacturing Purchasing Managers Index (PMI) rose to 57.4 in December versus 56.5 prior.
- The Indian Services PMI climbed to 60.8 in December from 58.4 prior. The Composite PMI jumped to 60.7 during the same report period from 58.6 in November.
- “The small rise in the headline manufacturing PMI in December was mainly driven by gains in current production, new orders, and employment,” said Ines Lam, economist at HSBC.
- The US S&P Global Composite PMI improved to 56.6 in December’s flash estimate versus 54.9 prior. Meanwhile, the Services PMI increased to 58.5 in December’s flash estimate from 56.1. The Manufacturing PMI eased to 48.3 from 49.7.
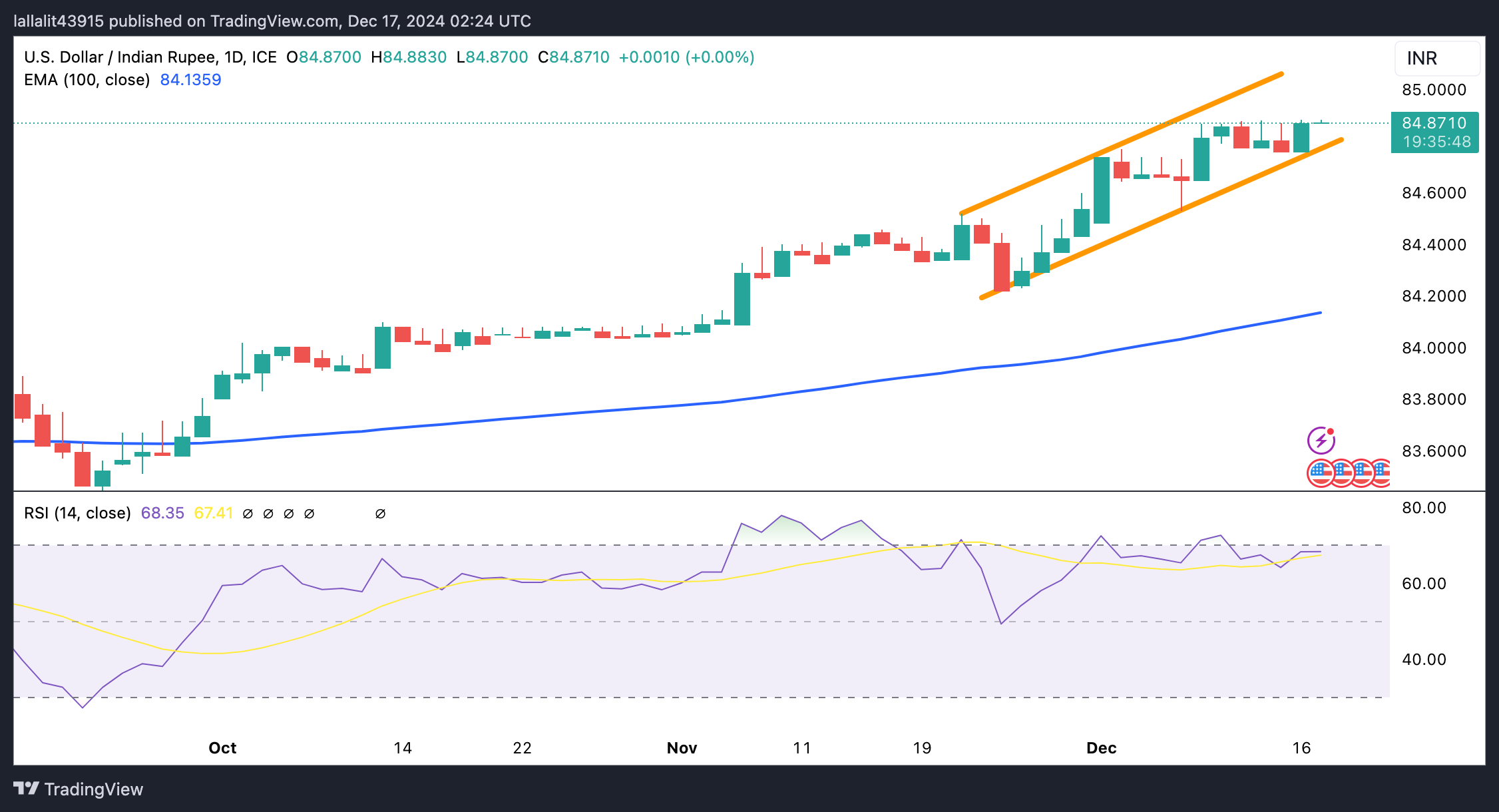
USD/INR keeps the bullish vibe in the longer term
The Indian Rupee trades weaker on the day. The constructive view of the USD/INR pair prevails, with the price holding above the key 100-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) on the daily chart. Additionally, the 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) is located above the midline near 68.35, supporting the buyers in the near term.
The ascending trend channel and the psychological level of 85.00 appear to be a tough nut to crack for bulls. Sustained bullish momentum could even take USD/INR to 85.50.
On the other hand, the first downside target to watch is the lower boundary of the trend channel of 84.80. A breach of this level could expose 84.22, the low of November 25. The potential support level for the pair is seen at 84.13, the 100-day EMA.
Indian economy FAQs
The Indian economy has averaged a growth rate of 6.13% between 2006 and 2023, which makes it one of the fastest growing in the world. India’s high growth has attracted a lot of foreign investment. This includes Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) into physical projects and Foreign Indirect Investment (FII) by foreign funds into Indian financial markets. The greater the level of investment, the higher the demand for the Rupee (INR). Fluctuations in Dollar-demand from Indian importers also impact INR.
India has to import a great deal of its Oil and gasoline so the price of Oil can have a direct impact on the Rupee. Oil is mostly traded in US Dollars (USD) on international markets so if the price of Oil rises, aggregate demand for USD increases and Indian importers have to sell more Rupees to meet that demand, which is depreciative for the Rupee.
Inflation has a complex effect on the Rupee. Ultimately it indicates an increase in money supply which reduces the Rupee’s overall value. Yet if it rises above the Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) 4% target, the RBI will raise interest rates to bring it down by reducing credit. Higher interest rates, especially real rates (the difference between interest rates and inflation) strengthen the Rupee. They make India a more profitable place for international investors to park their money. A fall in inflation can be supportive of the Rupee. At the same time lower interest rates can have a depreciatory effect on the Rupee.
India has run a trade deficit for most of its recent history, indicating its imports outweigh its exports. Since the majority of international trade takes place in US Dollars, there are times – due to seasonal demand or order glut – where the high volume of imports leads to significant US Dollar- demand. During these periods the Rupee can weaken as it is heavily sold to meet the demand for Dollars. When markets experience increased volatility, the demand for US Dollars can also shoot up with a similarly negative effect on the Rupee.
Information on these pages contains forward-looking statements that involve risks and uncertainties. Markets and instruments profiled on this page are for informational purposes only and should not in any way come across as a recommendation to buy or sell in these assets. You should do your own thorough research before making any investment decisions. FXStreet does not in any way guarantee that this information is free from mistakes, errors, or material misstatements. It also does not guarantee that this information is of a timely nature. Investing in Open Markets involves a great deal of risk, including the loss of all or a portion of your investment, as well as emotional distress. All risks, losses and costs associated with investing, including total loss of principal, are your responsibility. The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of FXStreet nor its advertisers. The author will not be held responsible for information that is found at the end of links posted on this page.
If not otherwise explicitly mentioned in the body of the article, at the time of writing, the author has no position in any stock mentioned in this article and no business relationship with any company mentioned. The author has not received compensation for writing this article, other than from FXStreet.
FXStreet and the author do not provide personalized recommendations. The author makes no representations as to the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of this information. FXStreet and the author will not be liable for any errors, omissions or any losses, injuries or damages arising from this information and its display or use. Errors and omissions excepted.
The author and FXStreet are not registered investment advisors and nothing in this article is intended to be investment advice.